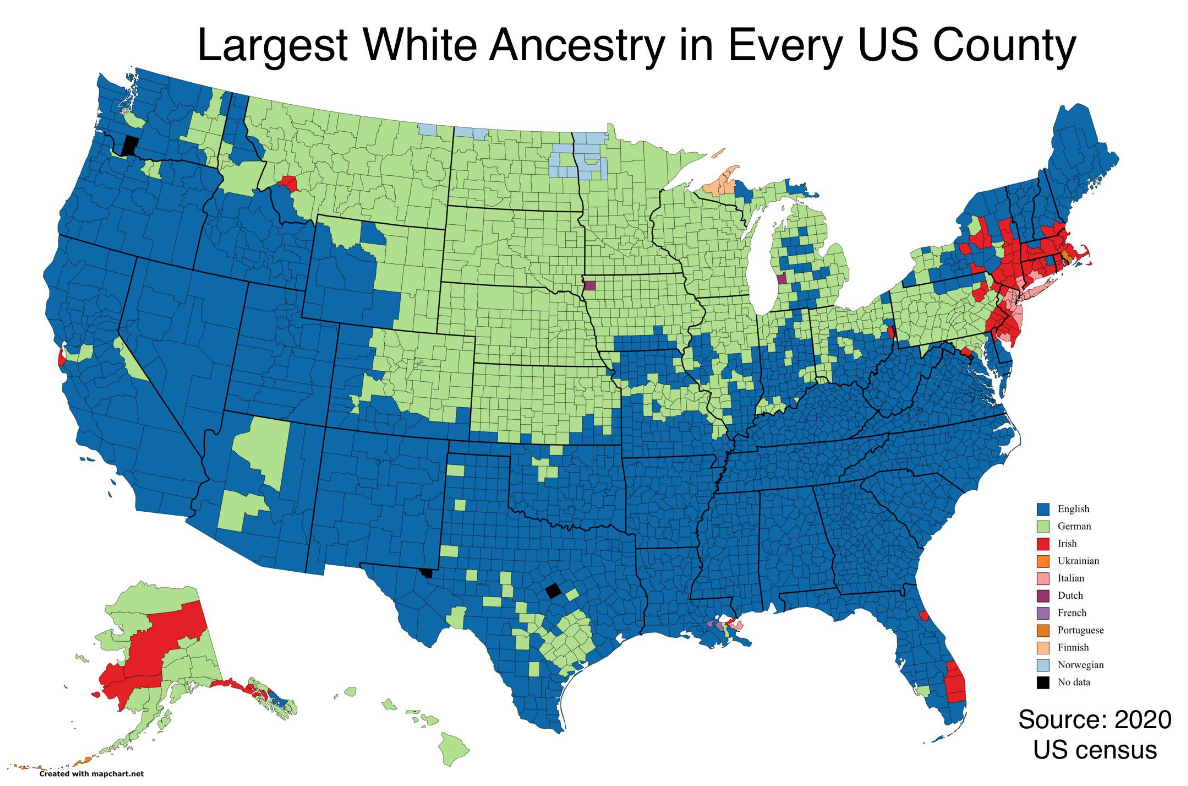
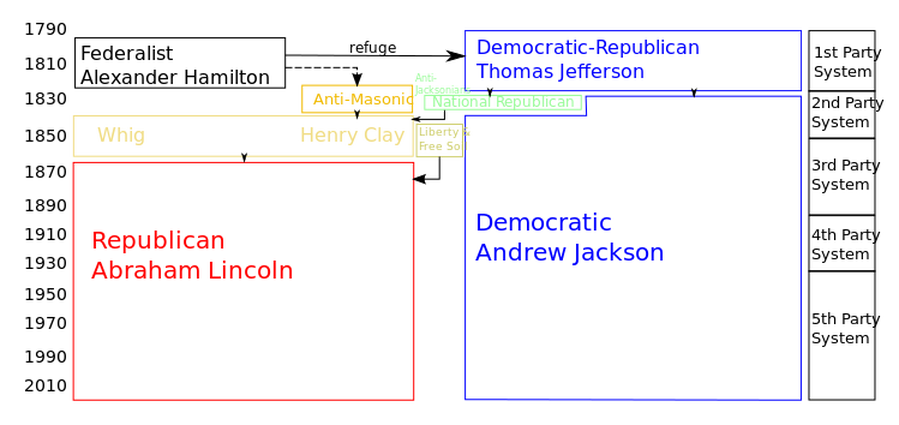
Key Period 4- Growth, conflict, reform
(1800-1848)
PRIMARY SOURCE READINGSkey period 4 agendaDay 1 Tuesday, October 3rd (Common Day)
HWP KP3 Due KP3 Exam Day 2 Wednesday, October 4th Go over Flipped Lecture 3.4 Washington to Jefferson next week Pass Out Papers & Explain Unit 4. SAQ Grading Activity Re-writes begin 10/5; OFFICE HOURS & 1st lunch only 10/5 Day 3 Friday, October 6th (SUB) FLIPPED Lecture 4.1 Growth and Conflict & 4.2 Manifest Destiny Day 4 Tuesday October 10th HIPPO 1 Andrew Jackson Essay Reading HIPPO 2 Indian Removal Essay Reading (read oyo) Finish 3.4 Lecture Notes Flipped Lecture 4.1 Growth and Conflict & 4.2 Manifest Destiny Day 5 Wednesday October 11th PSAT DAY Begin going over Lecture 4.1 in class Quiz 4.1 is Open Deadline: Nov 04, 2023 | 11:45 PM Day 6 Friday October 13th Finish Lecture 4.1 Growth and Conflict Flipped Lecture 4.2 Manifest Destiny Begin Lecture 4.3 Making of America Day 7 Tuesday, October 17th Continue 4.3 Making of America Pass back LEQ1 RW, & LEQ 2 writings Pickin Shark Tank Projects Hoo Ha Ha Begin Lecture 4.3 Making of America Day 8 Wednesday, October 18th Group Exam Re-take KP3 10/19 &10/20 Re-writes LEQ 1 (RW3 only) & LEQ 2 RW Begin Day 9 Friday October 20th Finish Lecture 4.3 Making of America Begin Lecture 4.4 Religious and Moral Reform Day 10 Tuesday October 24th Begin How to HIPPO the Practice DBQ KP2 DBQ- 3-4 Paragraph Essay Points 1. Context Point 2. Thesis Point 3. Three documents described/summarized Point 4. Four documents used to extend argument Point 5. Two documents HIPP'd correctly Point 6. Outside Information Point 7. #7/Synthesis/ Extra Point Break down new LEQ/DBQ Rubric KP2 DBQ Activity LEQ Activity Day 11 Wednesday October 25th Peer grading activity Pass back LEQ 1 Essay RW LEQ 2 RW continue 10/25-10/27 during 1st lunch & OH Day 12 Friday October 27th DBQ Assemble HWP Day 13 Tuesday October 31st Key Period 4 Exam & HWP Due Day 14 Wednesday, November 1st Shark Tank Presentations Day 15 Friday November 3rd Finish Shark Tank Presentations Begin KP5 material, pass out materials Quiz 4.1 is Open Deadline: Nov 04, 2023 | 11:45 PM Day 1 Tuesday November 7th Lecture 5.1 LecturesKP4 Key Terms/quiz yo selfffapush resourcesFUTURE FFA Resources
Causation Reconstruction http://nebula.wsimg.com/92307abfc4cd4074b945cfcca7b59d16?AccessKeyId=E9AACE2A0AB5B10EA5F6&disposition=0&alloworigin=1 Classroom Timeline brainstormWhat's Missing Still From Key Periods 1-4?
1. Samuel Slater: Textile mill using spinning jenny
2. Samuel Colt: Six Shooter Revolver 3. Eliphalet Remington: Rifle barrel 4. Samuel Morse: Telegraph 5. Robert Fulton: steamboat 6. Francis Cabot Lowell: Factory system using power loom 7. Eli whitney: interchangeable parts 8. Cyrus McCormick: mechanical reaper 9. John Deere: steel plow 10. Elias Howe: sewing machine 11. Crawford W. Long: ester anesthesia 12. Benjamin Wright: Erie Canal 13. Charles Goodyear: vulcanized rubber Period 2 Inventions
1- Hazey & Rooke 2- Louisa & Andrew 3- Hyrum, Derrick, & Ben 4- Ayush, Aaron, Alexis 5- Leo & Josh & Corwin 6- Bailey & Viri 7- Candace & Sorrelle 8- Rishi & Abhi 9- Audrey & Jackie 10- Prapti, Ishita, Kyra 11- Max & Jonathan 12- Nathan & Reese 13- Nathan & Jordan Period 4 Inventions
1- Avyu & Dipika 2- Sage & Salvador 3- Koby & Miguel 4- Angelique & Nathaly 5- Aarohi & Devon 6- Michelle & Elizabeth 7- Jason, Josh, Ethan 8- Stanley & Lu 9- Dongfeng & Jaideep 10- Max Aiden & Prithvi 11- Sam & Emily 12- Mark & Daniel 13- Jonathon & Carlos |
TEXTBOOK READINGSRead the text book Ch. 8-11
Unit 4 HomeworkUnit 4 Packet
1. HIPPOS 1-6 In Order (1,2 rank) 60 points 2. Unit 4 Quicksheet 250 points 3. USA Territorial Map 100 points 4. Guided Lecture Notes Completed 140 points 5. Key Period 4 Timeline of Key Events 50 points HW Packet worth 600 points Quiz 4.1Make sure you put (2) or (4) in front of your
first and last name when using Quizizz if you want to receive full credit. Quiz 4.1 is Open Deadline: Nov 04, 2023 | 11:45 PM 1.Ask participants to open joinmyquiz.com 2.And enter this code 8591 7255 PERIOD 4 (1800-1848)
|
kp4 exam re-take groups
|
2nd period
1. Josh DJ, Duenas, Sorrelle, Louisa, Aaron 2. Jonathan, Audrey, Nathan A, Rooke, Max 3. Ishita, Virdi, Prapti, Kyra, Jackie 4. Andrew, Hazey, Jordan, Hyrum, Abhi 5. Rishi, Ben, Alexis, Corwin, Reese 6. Candace, Derrick, Leo, Bailey, Ayush |
4th period
1. Dongfeng, Nathaly, Joshua, Salvador, Elizabeth 2. Sage, Carlos, Aiden, Devon, Koby 3. Jaideep, Daniel, Avyu, Dipika, Angelique 4. Mark, Prithvi , Samantha, Max 5. Jason, Stanley, Emily, Ethan 6. Miguel, Michelle, Aarohi, Lu |
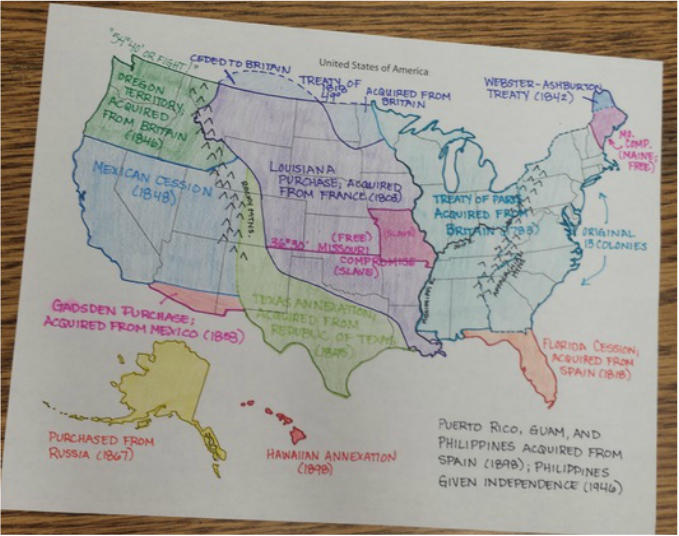
completed product
Your map should look like this. Add in the state abbreviations (CA, OR, MA, etc.) AND
the capitols of each of the states. This will be due next Friday October 30th
the capitols of each of the states. This will be due next Friday October 30th