Key Period 8 (1945-1980) &
Key Period 9 (1980-Present)
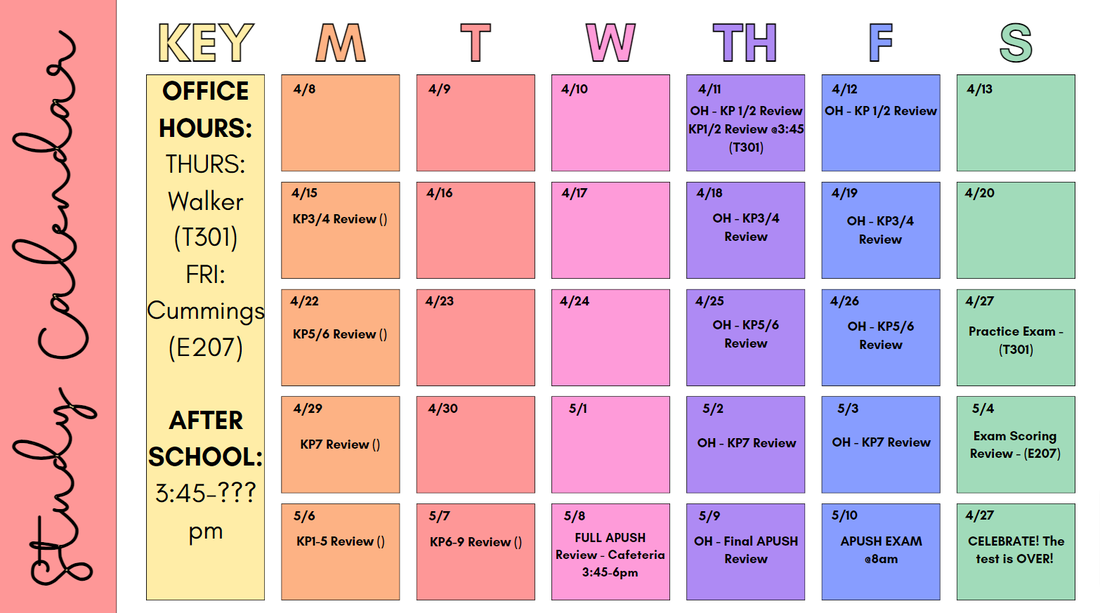
AgendaTuesday March 19th
HWP Due KP7B Exam & DBQ Day 1 Wednesday March 20th Pass out KP8 Material New Deal SAQ Grading Activity HIPPO 1 & HIPPO 2 Day 2 Friday March 22nd 8.1 The Cold War Day 3 Tuesday March 26th Go over DBQ & Grading of DBQ 8.2 The Korean War Begin 8.3 Cold War Comes Home Day 4 Wednesday March 27th KP7 Exam Group Re-take Day 5 Friday March 29th Assign KP8 Persons Project Causation DBQ Early Cold War (in-class) http://nebula.wsimg.com/2bbffe88c98d60fcc300dada264b2e16?AccessKeyId=E9AACE2A0AB5B10EA5F6&disposition=0&alloworigin=1 8.3 The Cold War Comes Home FLIPPED -Stalin to Kruschev -Space Race, Sputnik -2nd Red Scare -NSC/CIA + U2 Affair -Loyalty Review/HUAC -McCarthyism -Alger Hiss/Rosenbergs -Hollywood Blacklist/10 -The Crucible Spring Break April 1st-5th Spring Break Day 6 Tuesday April 9th Turn Causation Packets in for credit. 8.4 The Affluent Society Flipped Lecture 8.5 Begin Conformity in the 1950s Thesis Packet http://nebula.wsimg.com/3ade9f58a024c96d98e74cf8ef7e04c3?AccessKeyId=E9AACE2A0AB5B10EA5F6&disposition=0&alloworigin=1 8.5 The Nifty Fifties FLIPPED -Baby Boom -Levittown -GI BILL -Television/Automobile = Conformity Day 7 Wednesday April 10th Pass back Conformity Thesis Statements & discuss... Assign KP8 Persons Projects Turn in Conformity Thesis statement Packet Begin 8.6 Origins of the Civil Rights Day 8 Friday April 12th DBQ Finish 8.6 Origins of the Civil Rights Malcolm X Reading 8.7 The Young Fight Jim Crow Day 9 Tuesday April 16th Rally Schedule Finish 8.7 The Young Fight Jim Crow 8.8 Changing Laws Doesn't Always Change Minds Day 10 Wednesday April 17th Finish 8.8 Changing Laws Doesn't Always Change Minds Begin 8.9 Camelot and Crisis Day 11 Friday April 19th Pass back graded DBQs Finish 8.9 Camelot and Crisis Begin 8.10 Social Upheaval Day 12 Tuesday April 23rd Finish 8.10 Social Upheaval Day 13 Wednesday April 24th Begin 8.11 Vietnam 8.12 & 8.13 are flipped lectures Day 14 Friday April 26th KP8 Persons Projects Day 15 Tuesday April 30th Finish 8.11 Go over remaining Flipped Lectures Day 16 Wednesday May 1st Timeline Review Day in class. Continue to go over important 8.12 & 8.13 concepts Day 17 Friday May 3rd KP 8 HWP Due Group KP8 Exam Listen to Anti-Social Studies Podcast on Spotify, Episodes 21 & 22 as you take notes on 8.12 & 8.13 Heimler's History KP9 Day 18 Tuesday May 7th Day 19 May 8th Day 20 AP EXAM DAY May 10th 6:00 AM Review session in E207 before 7:30 AM walk-over. AP EXAM NOT UPDATED BELOW Tuesday May 14th -Go over AP Exam -Go over Final Project Begin Forrest Gump Wednesday May 15th Continue Forrest Gump Friday May 17th Returning APUSH Henretta Textbooks first 20 minutes of class. Pick Final Projects Finish Forrest Gump Tuesday May 21st Board games/research time/website help Wednesday May 22nd SUB Finish KP8 Persons Projects Friday May 24th SUB Thursday- Research day in library No School May 27th NO SCHOOL MEMORIAL DAY Tuesday May 28th Period 1 & Period 4 Final Exam Board games Wednesday May 29th Period 2 & Period 5 Final Exam Board games Thursday May 31st Period 3 & Period 6 Final Exam Board games No School Friday June 1st Possibilities
Go over 4 different prompts: http://nebula.wsimg.com/02144ca47a5f862352b10e55d99cfb63?AccessKeyId=E9AACE2A0AB5B10EA5F6&disposition=0&alloworigin=1 DBQ Breakdown: Thesis + Documents https://apprend.io/apush/apush-dbq-breakdown/ 13 Colonies Quiz (18 sec, 100%) https://online.seterra.com/en/vgp/3044 Khan Academy: Great Migration https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/ap-us-history/general-ap-us-history-skills-and-test-strategies/apush-examples/v/ap-us-history-dbq-example-1 Khan Academy LEQ: The New Deal https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/ap-us-history/general-ap-us-history-skills-and-test-strategies/apush-examples/v/ap-us-history-long-essay-example-1 Lectureshttps://faroutmagazine.co.uk/jimi-hendrix-national-anthem-woodstock-explanation-dick-cavett/
Key Period 9Final ProjectReagan
The New Right Cold War, Truman ---> Reagan Federal Spending, Liberalism vs Conservatism September 11th Engel, Epperson, and Roe Periodization 1980-93 (Reagan Era), 1993-Present (Modern Era) Reagan + Trump Campaign Slogan NAFTA vs TPP SDI Patriot Act Internet Globalization Consumerism (From Reddit)
[–]bacon_cake 293 points 6 hours ago Spend half a day in the shoes of an average person. Walk a mile through any town. Switch on any TV. Visit any website. The sheer effort that is spent consistently, constantly, cleverly, and relentlessly every single waking moment to try and convince us that we need to buy things we don't need is phenomenal. It's never ending, it's practically unavoidable, it starts the day we're born and seldom does a day go by that we're not subjected to it. It started with posters and slogans from marketing executives, now its evolved into an omnipresent force; it's algorithms, guerilla marketing, subliminal mood association, sports team sponsorships. For God's sake our gas pumps play video ads, we have ads between shows, ads before shows, ads during shows, product placement within shows, ads on Facebook, ads on reddit, ads in our newspapers, ads on our buses, trains, cars, billboards, and if we're within a month of superbowl we have ads for our fucking ads. The cleverest people and the richest people, they spend careers and lifetimes trying to make us spend. It's consumerism. It's brainwashing. And it's terrifying. Vocabularymake a trip through
|
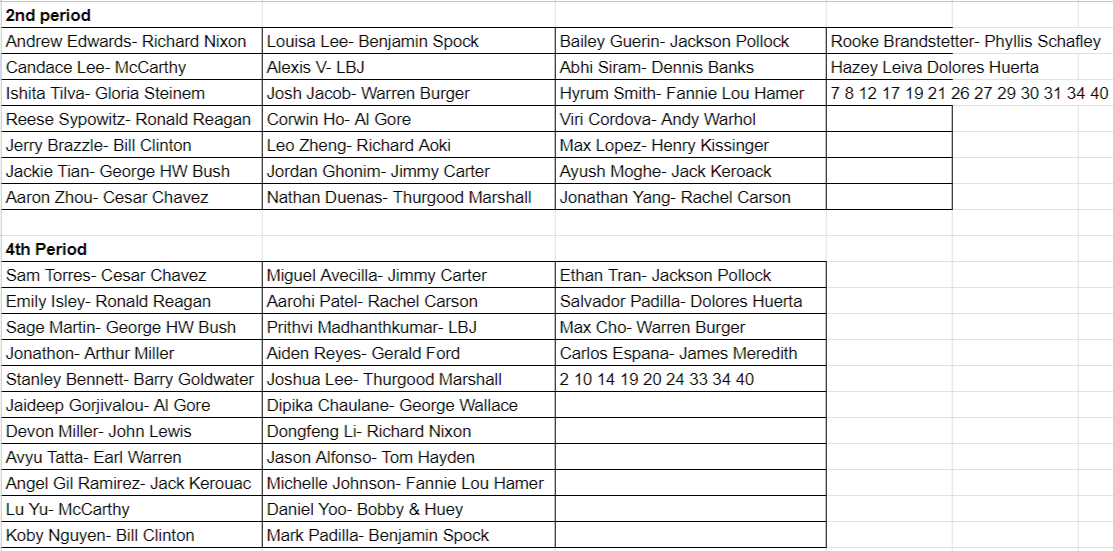
UNIT 8 HOMEWORKPrimary Source Documents LinkSix Degrees of Separation kp8 Historical Persons ProjectExpectations: Make a short video and house it on a Smore Website. Explain in less than two minutes (including video) the historical significance of your person, and how/why they are relevant to APUSH. Try and link them to others on the page if it makes it easier for you to create something. 100 points
"It's time to fight back that's what Huey said, two shots in the dark now Huey's dead" Tie them to the Key Concept Outline. Presentations are due by April 26th before class begins. quiz 8.1 & 9.1Deadline: 11:45pm April 27th Saturday
Deadline: 11:45pm, May 4th Saturday
April & may review sessions
Wednesday May 8th cafeteria
PERIOD 8 (1945-1980)PERIOD 8:
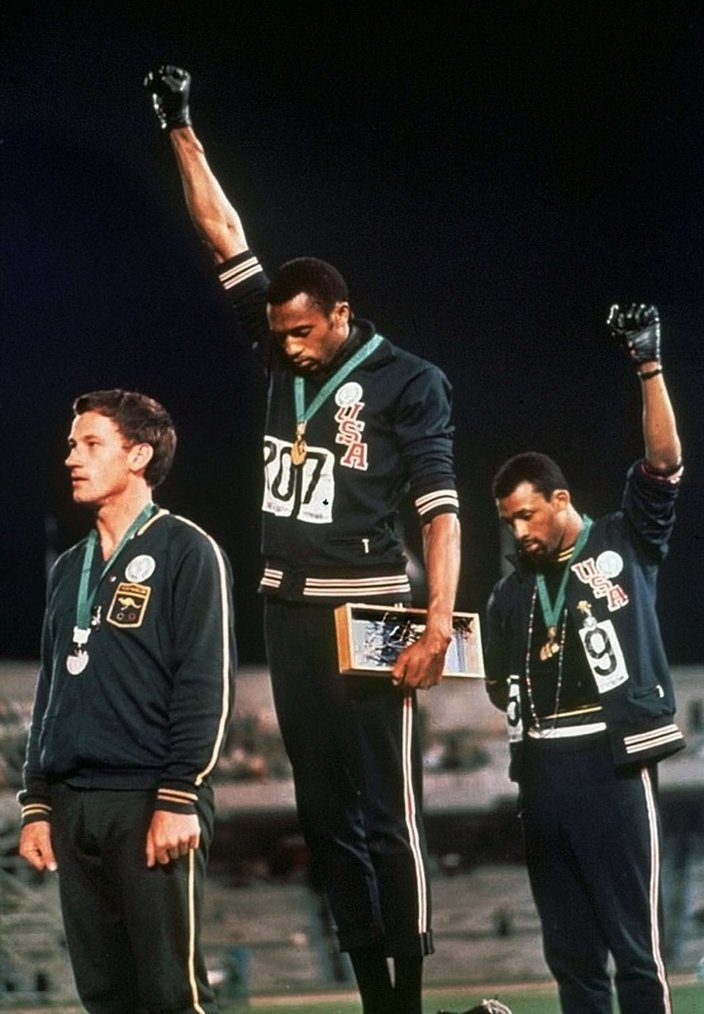
1945–1980 After World War II, the United States grappled with prosperity and unfamiliar international responsibilities while struggling to live up to its ideals. Key Concept 8.1: The United States responded to an uncertain and unstable postwar world by asserting and attempting to defend a position of global leadership, with far-reaching domestic and international consequences. I. After World War II, the United States sought to stem the growth of Communist military power and ideological influence, create a stable global economy, and build an international security system. A. The United States developed a foreign policy based on collective security and a multilateral economic framework that bolstered non-Communist nations. B. The United States sought to “contain” Soviet-dominated communism through a variety of measures, including military engagements in Korea and Vietnam. • development of hydrogen bomb • massive retaliation • space race C. The Cold War fluctuated between periods of direct and indirect military confrontation and periods of mutual coexistence (or détente). II. As the United States focused on containing communism, it faced increasingly complex foreign policy issues, including decolonization, shifting international alignments and regional conflicts, and global economic and environmental changes. A. Postwar decolonization and the emergence of powerful nationalist movements in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East led both sides in the Cold War to seek allies among new nations, many of which remained nonaligned. Key Concept 8.1 B. Cold War competition extended to Latin America, where the United States supported non-Communist regimes with varying levels of commitment to democracy. C. Ideological, military, and economic concerns shaped U.S. involvement in the Middle East, with several oil crises in the region eventually sparking attempts at creating a national energy policy. • Suez Crisis, Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) III. Cold War policies led to continued public debates over the power of the federal government, acceptable means for pursuing international and domestic goals, and the proper balance between liberty and order. A. Americans debated policies and methods designed to root out Communists within the United States even as both parties tended to support the broader Cold War strategy of containing communism. B. Although the Korean conflict produced some minor domestic opposition, the Vietnam War saw the rise of sizable, passionate, and sometimes violent antiwar protests that became more numerous as the war escalated. C. Americans debated the merits of a large nuclear arsenal, the “military-industrial complex,” and the appropriate power of the executive branch in conducting foreign and military policy. Key Concept 8.2: Liberalism, based on anticommunism abroad and a firm belief in the efficacy of governmental and especially federal power to achieve social goals at home, reached its apex in the mid- 1960s and generated a variety of political and cultural responses. I. Seeking to fulfill Reconstruction-era promises, civil rights activists and political leaders achieved some legal and political successes in ending segregation, although progress toward equality was slow and halting. A. Following World War II, civil rights activists utilized a variety of strategies — legal challenges, direct action, and nonviolent protest tactics — to combat racial discrimination. • Fannie Lou Hamer, John Lewis, Thurgood Marshall B. Decision-makers in each of the three branches of the federal government used measures including desegregation of the armed services, Brown v. Board of Education, and the Civil Rights Act of 1964 to promote greater racial justice. C. Continuing white resistance slowed efforts at desegregation, sparking a series of social and political crises across the nation, while tensions among civil rights activists over tactical and philosophical issues increased after 1965. II. Stirred by a growing awareness of inequalities in American society and by the African American civil rights movement, activists also addressed issues of identity and social justice, such as gender/sexuality and ethnicity. A. Activists began to question society’s assumptions about gender and to call for social and economic equality for women and for gays and lesbians. • The Feminine Mystique, Gloria Steinem Key Concept 8.2 B. Latinos, American Indians, and Asian Americans began to demand social and economic equality and a redress of past injustices. C. Despite the perception of overall affluence in postwar America, advocates raised awareness of the prevalence and persistence of poverty as a national problem, sparking efforts to address this issue. III. As many liberal principles came to dominate postwar politics and court decisions, liberalism came under attack from the left as well as from resurgent conservative movements. A. Liberalism reached its zenith with Lyndon Johnson’s Great Society efforts to use federal power to end racial discrimination, eliminate poverty, and address other social issues while attacking communism abroad. B. Liberal ideals were realized in Supreme Court decisions that expanded democracy and individual freedoms, Great Society social programs and policies, and the power of the federal government, yet these unintentionally helped energize a new conservative movement that mobilized to defend traditional visions of morality and the proper role of state authority. • Griswold v. Connecticut, Miranda v. Arizona C. Groups on the left also assailed liberals, claiming they did too little to transform the racial and economic status quo at home and pursued immoral policies abroad. • Students for a Democratic Society, Black Panthers Key Concept 8.3: Postwar economic, demographic, and technological changes had a far-reaching impact on American society, politics, and the environment. I. Rapid economic and social changes in American society fostered a sense of optimism in the postwar years as well as underlying concerns about how these changes were affecting American values. A. A burgeoning private sector, continued federal spending, the baby boom, and technological developments helped spur economic growth, middle-class suburbanization, social mobility, a rapid expansion of higher education, and the rise of the “Sun Belt” as a political and economic force. B. These economic and social changes, in addition to the anxiety engendered by the Cold War, led to an increasingly homogeneous mass culture as well as challenges to conformity by artists, intellectuals, and rebellious youth. • Beat movement, The Affluent Society, rock and roll music C. Conservatives, fearing juvenile delinquency, urban unrest, and challenges to the traditional family, increasingly promoted their own values and ideology. II. As federal programs expanded and economic growth reshaped American society, many sought greater access to prosperity even as critics began to question the burgeoning use of natural resources. A. Internal migrants as well as migrants from around the world sought access to the economic boom and other benefits of the United States, especially after the passage of new immigration laws in 1965. B. Responding to the abuse of natural resources and the alarming environmental problems, activists and legislators began to call for conservation measures and a fight against pollution. Key Concept 8.3 • Rachel Carson, Clean Air Act III. New demographic and social issues led to significant political and moral debates that sharply divided the nation. A. Although the image of the traditional nuclear family dominated popular perceptions in the postwar era, the family structure of Americans was undergoing profound changes as the number of working women increased and many social attitudes changed. B. Young people who participated in the counterculture of the 1960s rejected many of the social, economic, and political values of their parents’ generation, initiated a sexual revolution, and introduced greater informality into U.S. culture. C. Conservatives and liberals clashed over many new social issues, the power of the presidency and the federal government, and movements for greater individual rights. • Watergate, Bakke v. University of California, Phyllis Schlafly |